高级中学教师资格证考试大纲《英语学科知识与教学能力》
中学教师资格证考试大纲一、考试目标
1. 英语学科知识与能力
具有扎实的英语语言基础知识和语言沟通能力;具备从事高中英语教学所需要的英语语言能力;能理解有关英语国家的语言、历史和文化等相关知识。
2.英语学科教学知识与能力
掌握基本的、适合高中英语教学的学科教学知识和英语课程标准知识,并能用以指导高中英语教学。
3.英语学科教学设计能力
能够根据英语学科特点,针对高中学生的认知特点、语言水平和学习需要选择并设计合理的教学内容,形成完整合理的教学方案。
4. 英语学科教学实施能力
理解高中英语课堂教学实施的基本原则和方法,具备实施语言课堂教学的基本能力;能够依据教学设计,根据教学实际情况,采用恰当的教学手段,引导学生进行有效学习。
5. 英语学科教学评价知识与能力
了解高中英语课堂教学评价的基本知识和方法,能够对学生的语言学习进行恰当的评价;了解教学反思的基本方法和策略,能够对自己的课堂教学实践进行反思,提出改进的思路。
中学教师资格证考试大纲二、考试模块内容与要求
(一) 语言知识与能力
1.掌握英语语言的基础知识,了解语言学研究中与语言教学相关的基本概念和内容,并能在课堂教学中加以运用。
2.具有良好的英语语言运用能力,包括用英语进行书面表达、获取教学资源和信息、表达思想情感和与学生良好沟通的能力;能够筛选并改编适合高中学生英语水平的教学材料。
3.能在语篇中理解英语国家的语言、历史和文学等相关的社会文化知识。
(二)语言教学知识与能力
1.了解英语教学基本理论,理解语言观、语言学习观、语言教学观等对高中英语教学的指导作用。
2.理解《普通高中英语课程标准(实验)》的目标内容(语言技能、语言知识、情感态度、学习策略和文化意识),以及课程标准的其他相关知识,并能在教学设计与实施中运用。
3.掌握英语语言知识(语音、词汇、语法等)的教学基本原则、讲解和练习方法。
4.掌握英语语言技能(听、说、读、写)教学的基本原则和训练方法。
5.能结合英语社会文化语境,设计并实施英语知识和技能的教学与训练。
(三)教学设计
1.了解高中学生的认知特征、已有的英语知识、语言能力和学习需求,能够说明教学内容与学生已学知识之间的联系。
2.理解课程标准的目标要求,能够根据学生的特点选择恰当的教学内容。
3.掌握根据恰当的教学内容,设定合理、明确与具体的教学目标。
4.能根据教学目标,创设教学情景、设计有效的教学活动、安排合理的教学过程、编制辅助教学材料。
5.能够根据教学内容和教学过程,设计有效的学习评估活动。
(四)教学实施与评价
1.掌握英语课堂教学的基本步骤与方法,能够创设教学情景,激发学习动机,引导学生参与语言学习活动。
2.掌握指导学生学习的方法和策略,能依据英语学科特点和学生的认知特征,根据教学实际情况,恰当地运用语言讲解、互动练习、提问、反馈等方法,帮助学生有效学习。
3.掌握课堂管理基本方法,熟悉课堂活动常用组织形式,能在教学活动中以学生为中心组织教学,能在课堂教学的不同阶段发挥教师的作用。
4.掌握课堂总结的方法,能适时地对教学内容进行归纳、总结与评价,科学合理地布置作业。
5.了解现代教育技术,能够针对不同英语课型,整合多种资源和辅助教学手段进行有效教学。
6.了解高中英语教学形成性评价和终结性评价的知识与方法,并在教学中合理运用。
7.掌握教学案例评析的基本方法,能够对所给的教学案例进行评价。
8.了解教学反思的基本方法和策略,能够对自己的教学进行反思并提出改进思路。
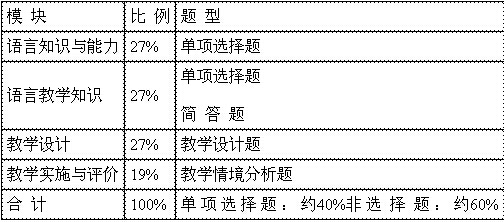
中学教师资格证考试大纲三、试卷结构
中学教师资格证考试大纲四、 题型示例
I. 语言知识与能力
1. 单项选择题(语言知识)
(1)Thousands of ex-army officers have found _________ jobs in private security firms in the US.
A. lucrative B. ludicrous
C. longish D. lucky
(2)The manager persuaded the team to play the game. What actually happened according to this statement?
A. The manager played hard.
B. The team played hard.
C. The team actually did not play.
D. The manager actually did not play.
II. 单项选择题(阅读理解)
READING COMPREHENSION
Read the following passage and answer the questions below.
Transcribe the sound represented by the underlined letter(s) in the words and then describe it. (10 points)
Medicine in Britain
In Britain there is a national health service (the NHS), which is paid for by taxes and national insurance, and in general people do not have to pay for medical treatment. Every person is registered with a doctor in their local area, known as a general practitioner or GP. This means that their name is on the GP’s list, and they may make an appointment to see the doctor or may call the doctor out to visit them if they are ill. People sometimes have to pay part of the cost of drugs that the doctor prescribes. GPs are trained in general medicine but are not specialists in any particular area. If a patient needs to see a specialist doctor, they must first go to their GP and then the GP will make an appointment for the patient to see a specialist at a hospital or clinic.
Although everyone in Britain can have free treatment under the NHS, it is also possible to have private medical care, for which one has to pay. Some people have private health insurance to help them pay for private treatment. Under the NHS, people who need to go to a hospital (e.g., for an operation) may have to wait a long time. If they pay for the treatment, they will probably get it more quickly.
Anyone who is very ill can call an ambulance and be taken to a hospital for free emergency medical treatment. Ambulances are a free service in Britain.
(1)In the British medicare system, a doctor who serves a local community is more likely to be paid by ________.
A. patients and their families B. everyone in the country
C. insurance companies D. tax payers and personal contributions
(2) Some people opt for private medical service because it is ________.
A. quick and free
B. long waiting list and paid service
C. short waiting time and paid medicare
D. short waiting time and better medicine
III. 语言教学知识
1.单项选择题
Which of the following activities belongs in communicative practice?
A. Repeating sentences that the teacher says.
B. Doing oral grammar drills.
C. Reading aloud passages from the textbook.
D. Giving instructions so that someone can use a new machine.
2. 简答题(中文作答)
(1)请辨析下列两个句子的不同点并解释原因。
Did you eat something this evening?
Did you eat anything this evening?
(2)英语教师应该如何看待并处理学生的语言错误?请举例说明。
IV.教学设计题
请根据以下提供的信息和语言素材进行教学设计。本题用英文作答。具体要求是:根据所提供的语言素材设计教学活动,要求教学设计目标具体、教学内容分析恰当、教学重点和难点突出、教学过程完整、师生任务明确。
学生概况:本班为中等城市普通学校高中一年级的学生,班级人数为40人。多数学生已具备一定的英语语言能力。学生能够积极参与课堂活动,合作意识较强。
教学时间:45分钟
语言素材:(加粗单词为学生首次接触的词汇)
The Road to Modern English
At the end of the 16th century, above five to seven million people spoke English. Nearly all of them lived in England. Later in the next century, people from England made voyages to conquer other parts of the world and because of that, English began to be spoken in many other countries. Today, more people speak English as their first, second or a foreign language than ever before.
Native English speakers can understand each other even if they don’t speak the same kind of English. Look at this example:
British Betty: Would you like to see my flat?
American Amy: Yes, I’d like to come up to your apartment.
So why has English changed over time? Actually all languages change and develop when cultures meet and communicate with each other. At first, the English language spoken in England between about AD 450 and 1150 was very different from the English spoken today. It was based more on German than the English we speak at present. Then gradually between about AD 800 and 1150, English became less like German because those who ruled England spoke first Danish and later French. These new settlers enriched the English language and especially its vocabulary. So by the 1600s Shakespeare was able to make use of a wider vocabulary than ever before. In 1620 some British settlers moved to America. Later in the 18th century some British people were taken to Australia too. English began to speak in both countries.
Finally by the 19th century the language was settled. At that time two big changes in English spelling happened: first Samuel Johnson wrote his dictionary and later Noah Webster wrote The American Dictionary of English Language. The latter gave a separate identity to American English Spelling.
English now is also spoken as a foreign or second language in South Asia. For example, India has a very large number of fluent English speakers because Britain ruled India from 1765 to 1947. During that time English became the language for government and education. English is also spoken in Singapore and Malaysia and countries in Africa such as South Africa. Today the number of people learning English in China is increasing rapidly. In fact, China may have the largest number of English learners. Will Chinese English develop its own identity? Only time will tell.
V.教学情景分析题(中文作答)
分析以下教学片段:
T: What did your mummy do yesterday, Wang Lin?
S: My mummy buyed the dress for me.
T: Oh, that is nice, your Mummy bought it for you, did she?
S: Yes.
T: Where did she buy it?
S: She buyed it in town.
T: Oh, she bought it in town for you. Well, it is very nice.